What is the difference between ASME B16.36 and ASME B16.5 flanges?
Recently, Haihao Group produced a batch of ASME B16.36 orifice flanges for Singapore customers. In industrial piping systems, choosing the right flange type is crucial for system performance, safety and flow measurement accuracy. The most common one is the ASME B16.5 flange, which is widely used for general pipe connections. What is the difference between ASME B16.36 orifice flanges and ASME B16.5 flanges? Let’s take a look.
What is ASME B16.36?
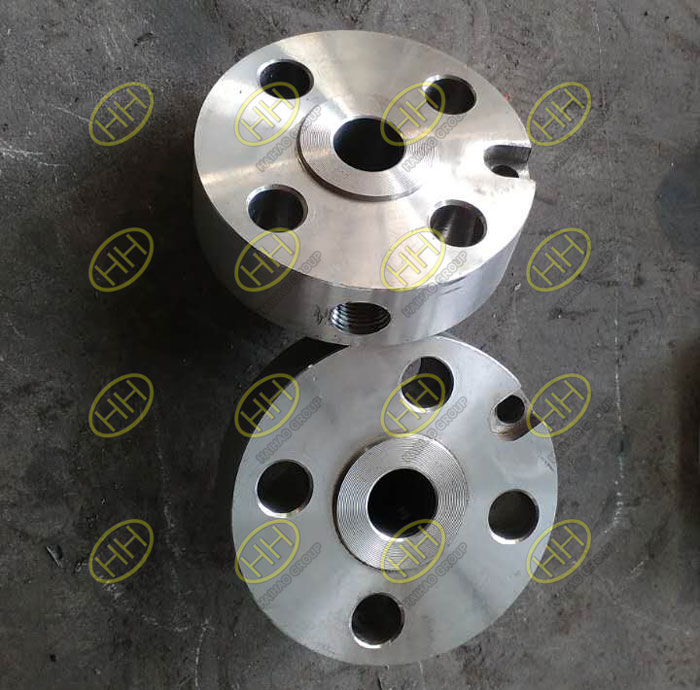
ASME B16.36 is the standard that covers orifice flanges, which are specially designed for differential pressure flow measurement using orifice plates. These flanges feature integrated tapping holes that allow for direct connection to pressure transmitters and other instrumentation.
Key Features of ASME B16.36 Orifice Flanges:
1.Integrated pressure tap holes (typically 1/2″ NPT) for flow measurement
2.Designed to be used in pairs, with an orifice plate and gasket sandwiched between them
3.Supports pressure classes from Class 300 to Class 2500
4.Available with Raised Face (RF) or Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) sealing surfaces
5.Dimensional compatibility with ASME B16.5 flanges
Applications:
Ideal for systems requiring accurate fluid or gas flow measurement, including:
- Oil & Gas processing
- Petrochemical plants
- Power generation pipelines
What is ASME B16.5?
ASME B16.5 is the general flange standard covering a wide range of pipe flanges and flanged fittings for use in various pressure classes and piping sizes.
Key Features of ASME B16.5 Pipe Flanges:
1.Covers flange types such as Weld Neck (WN), Slip-On (SO), Socket Weld (SW), Threaded (TH), Lap Joint (LJ), and Blind (BL)
2.Size range: 1/2″ to 24″
3.Pressure classes from Class 150 to Class 2500
4.Sealing surfaces: RF, RTJ, and Flat Face (FF)
5.No pressure tap holes or flow measurement design
Applications:
General pipe-to-pipe, pipe-to-valve, or pipe-to-equipment connections
Widely used in oil & gas, chemical, water treatment, and HVAC systems
ASME B16.36 vs. ASME B16.5: Key Differences
| Feature | ASME B16.36 (Orifice Flange) | ASME B16.5 (Pipe Flange) |
| Design Purpose | Built for differential flow measurement | General pipeline connection |
| Pressure Tap Holes | Required (angle or flange tap) | Not included |
| Pairing | Used in pairs to sandwich orifice plate | Typically used as individual flanges |
| Dimensional Base | Based on ASME B16.5 | Independent standard |
| Application | Flow monitoring in process systems | Standard pipe connections |
From the above comparison we can know ASME B16.36 is a functional extension of ASME B16.5
ASME B16.36 flanges build upon the dimensional and pressure class framework of ASME B16.5, but introduce tapping holes to accommodate orifice plates and measurement instruments. This makes B16.36 a special-purpose flange tailored for flow measurement, while B16.5 remains the go-to standard for general flange applications.
How to select the Right Flange?
| Use Case | Recommended Standard |
| Need to install orifice plates for flow measurement | ASME B16.36 |
| Standard pipe or equipment connection with no flow monitoring | ASME B16.5 |
For accurate differential pressure measurement, orifice flanges must be used in conjunction with orifice plates manufactured to ASME MFC-3M standards.
Choosing between ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.36 depends entirely on the intended application. While B16.5 offers versatility for general connections, B16.36 is essential for precision flow control using orifice plates. Both standards are often used together in large-scale piping systems, with B16.36 flanges perfectly matching B16.5 dimensions and sealing types—ensuring seamless integration and system reliability.